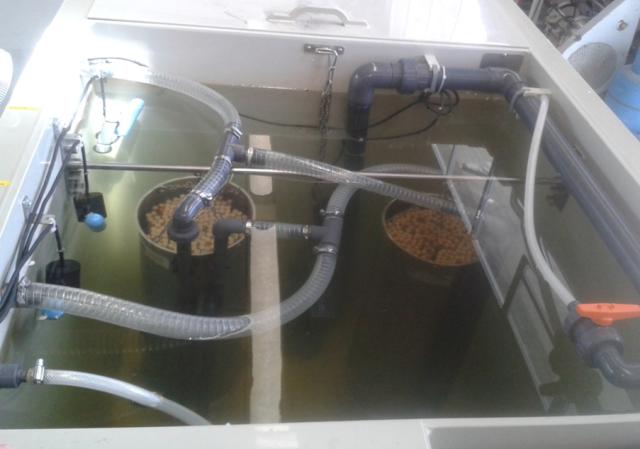
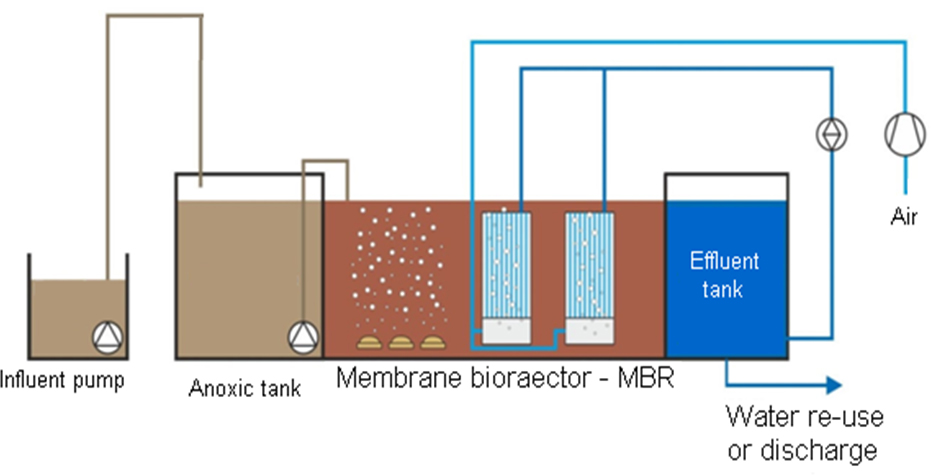
Working principles
Aerobic membrane bioreactors combine the advantages of conventional activated sludge (CAS) wastewater treatment systems with micro/ultra-membrane filtration.
This is a proven technology in a Western context. When implemented in India, new challenges need to be faced, including the operation under non-standardized and non-reliable receiving wastewaters, and excessive high temperatures. This technology also needs high appropriate maintenance. Therefore a pilot-scale movable MBR will be constructed and provided with low energy, submersible membranes for the evaluation of different operational regimes.
Main goals
MBRs combine aerobic bio-treatment with membrane separation, thus:
- Clarified, mostly disinfected effluent: Low turbidity, bacteria, Total Suspended Solids (TSS) and organic content
- Small footprint plant. Shorter Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT)
- Bulking problems become less relevant. Longer Solids Retention Time (SRT) with less sludge production
- Hydraulic and solids retention time are uncoupled
- Intensive bio-treatment provided
Test results and evaluation
Wastewater treatment and reuse
The system was installed and operated at IIT Delhi waste treatment labs using Barapullah drain wastewater. The purpose of testing this technology is that it is a benchmark for innovative technologies to compare to. In addition the set up was to assess whether trace organics such as pharmaceutical residues and pesticides are being removed adequately by the technology.
The MBR reactor, which had been ready for operation since the end of 2002, underwent continuous minor improvements, including the addition of a refrigerator to prevent biological degradation in the feeding tank before reaching the MBR tank.
From March 22 to May 11, 2023, the reactor operated at a flowrate of 1.5 L/day, aiming to establish sufficient biomass without disrupting membrane filtration. Preliminary results indicated its performance, showcasing COD removal, pH maintenance within municipal wastewater standards, and stable operation at an elevated temperature of approximately 28°C.
Notably, influent total COD from the Barapullah drain was relatively low, and the MBR effectively reduced it to around 29 mg/L due to the microfiltration membrane. Despite the low flowrate and non-continuous operation, the COD removal results were promising, suggesting potential for improved efficiency when operating at a higher flowrate.
For more details, consult the deliverable report*:
Laboratory test reports and fact sheets on water treatment technology and reuse
* The deliverable report is still under review and has not yet been approved by the European Commission. The final approved version will be uploaded as soon as possible.



